Technical
TECH TUESDAY: Why Red Bull could hit the ground running in 2020

Share

Max Verstappen’s victory in Brazil underlined how Red Bull are ending this season on a high. The pattern of their 2019 season is much as it was two years ago – beginning each season with a significant aerodynamic problem but aggressively developing their way out of it to end the year as arguably the fastest car. The season in between – 2018 – had a different pattern, as the RB14 was generally pretty competitive from the off.
Is there a technical factor driving these patterns? There were separate specific technical reasons – a wind tunnel modelling error in the case of 2017 – but it may be significant that both 2017 and ’19 featured major aerodynamic regulation changes, which forced Red Bull away from what had been very productive paths in both cases.
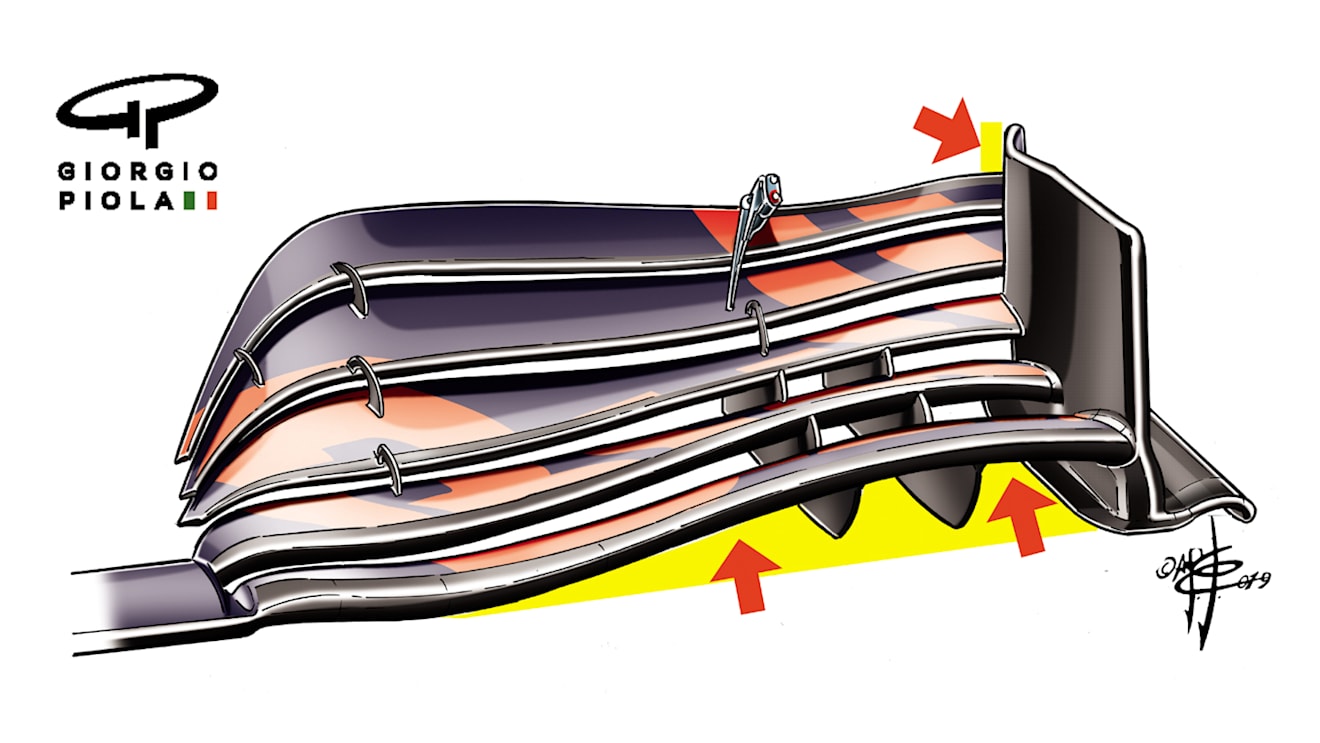
READ MORE: The wing designs winning out as focus shifts to 2020
Even though all the F1 cars may look ostensibly similar, each of the top three teams has their own very distinct aerodynamic philosophy and it seems that of Red Bull may just be more sensitive than the others and not as adaptable to change.

For many years, Red Bull’s aerodynamic foundation has relied upon a particularly high-rake angle. At low speeds the car runs nose-down and then as the squaring-with-speed downforce presses the car down, it runs flatter at high speeds.
This can work spectacularly well in that angling the floor from low at the front to high at the back creates greater negative pressure (ie pulling the car down) from the underfloor by funnelling the air through it faster. The amount of downforce generated by the underbody is, broadly speaking, a multiple of the floor area and speed of the airflow.
READ MORE: 5 Reasons We Love... The Abu Dhabi Grand Prix
Another aerodynamic advantage of a high-rake car is that the front wing can be made more efficient, as its elements meet the air with an angle of attack which induces greater downforce and then, at higher speeds down the straights (and in faster corners where the aero balance needs to be more rearwards to give stability) the car flattens out, giving a less aggressive front wing angle and a reduction in drag level.
1 / 2
The limitation defining how much rake can be run before it begins to have a negative effect is at what point the airflow through and around the diffuser stalls as the car speed lowers. As this happens and the tail of the car rises up, so the gap between the ground and diffuser increases just as the air speed is slowing and eventually reaches a point where it stops flowing, reducing the downforce at the rear.
READ MORE: How the top teams are juggling 2019, 2020 and 2021 car development
The more flow that can be induced over and around the diffuser, the longer the airflow coming through the diffuser from the underfloor will stay attached as the ride height increases as the speed comes down. A crucial part of Red Bull’s aero philosophy is creating a sharply tapered-in upper body at the rear with plenty of space around that in-cut. The in-cut increases the airflow’s speed, the space gives greater airflow capacity, both in the aid of deferring the diffuser stall as long as possible and thereby maximising the feasible degree of rake that can be run.
With the regulation change of 2017 the cars were made significantly wider and the tyre width was increased. This made it much more difficult to outwash the airflow around the front tyre – and to keep it out-washed and not to be sucked towards the more powerful wider underfloor.

The 2017 Red Bull challenger, RB13, evolved into a formidable F1 car
Aerodynamicists employed many tricks to do this, among them more powerful and intricate barge boards. But because the wider wind tunnel model of the 2017 car put it in closer proximity to the wind tunnel’s walls, the wind tunnel results were not realistic, exaggerating the drag penalty. It led Red Bull to believe they could not use very powerful barge boards. As a result the early RB13 lacked downforce. It was quickly developed once the issue had been identified and its late-season form was superb.
WATCH: How Red Bull evolved the RB15 into a race winner
The 2019 regulation change banished many of the aerodynamic tools that Red Bull had utilised so well in endowing their 2018 car with great performance. The front wings were simplified, blown axles banned, under-nose vanes limited to two per side, front brake ducts reduced in size (and therefore aerodynamic effectiveness) and the barge boards were lowered. Just as in 2017, Red Bull began the season over 1s off the pace as they had been loading those components arguably harder than anyone else.
With very little regulation change for next year, Red Bull might realistically be expected to hit the ground running rather better than they did in the recent odd-numbered years.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
News What tyres will the teams and drivers have for the 2025 Spanish Grand Prix?
News 'We put everything together when it mattered' – Ocon thrilled with return to the points in Monaco
News ‘It’s not a tension’ – Vasseur downplays rift rumours between Hamilton and race engineer Adami as he praises Leclerc’s Monaco podium
News ‘This is just the start’ – Stella backs Norris to hit top form after ‘cold blood’ Monaco victory